Contents

Source: Fosco Connect
<>
Understanding Multi-stage Fiber Amplifiers
Introduction
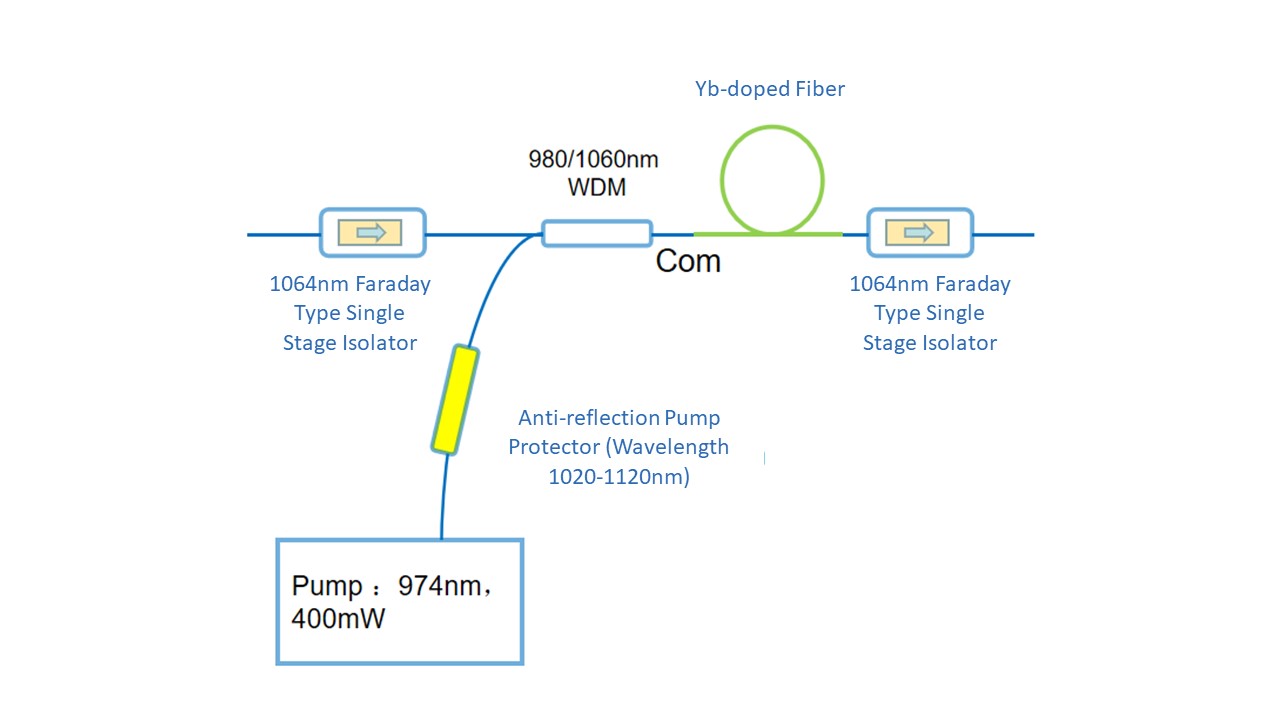
Multi-stage fiber amplifiers are setups containing multiple active fibers and are used for various reasons in fiber amplifier systems.
Need for Different Mode Areas
In fiber amplifier systems, different parts of the active fibers experience varying optical powers or pulse energies. Large mode areas are required for the final power amplifier stage to mitigate nonlinear effects and improve pump absorption. In contrast, smaller mode areas are preferred for low-power preamplifiers to enhance gain efficiency and power conversion efficiency.
Need for Different Pumping Options
Using different fibers in multi-stage amplifiers allows for optimized pumping strategies, such as direct core pumping for preamplifiers and cladding pumping for power amplifiers. Additional pump light can also be injected into multiple fiber ends for enhanced power.
ASE Suppression
To prevent excessive amplified spontaneous emission (ASE), multi-stage amplifiers employ techniques like optical bandpass filters, Faraday isolators, time gating with optical switches, and polarizers to suppress unwanted ASE between stages.
Minimizing Amplifier Noise
Combining a low-noise core-pumped preamplifier with a high-power double-clad fiber power amplifier can improve the overall noise figure of the amplifier system.
Protection and Monitoring
Using Faraday circulators, one can extract signal light returning from the power amplifier to prevent damage to preceding stages. Monitoring power levels between stages is essential for detecting and addressing operational issues promptly.
Gain Flattening
For applications requiring flat gain profiles, gain-flattening filters can be inserted between amplifier stages to minimize variations in gain within a spectral window. Combining fibers with different core compositions can also help achieve a broader gain spectrum.
Source: SIMTRUM.com
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



