Contents
Source: Edmund Optics
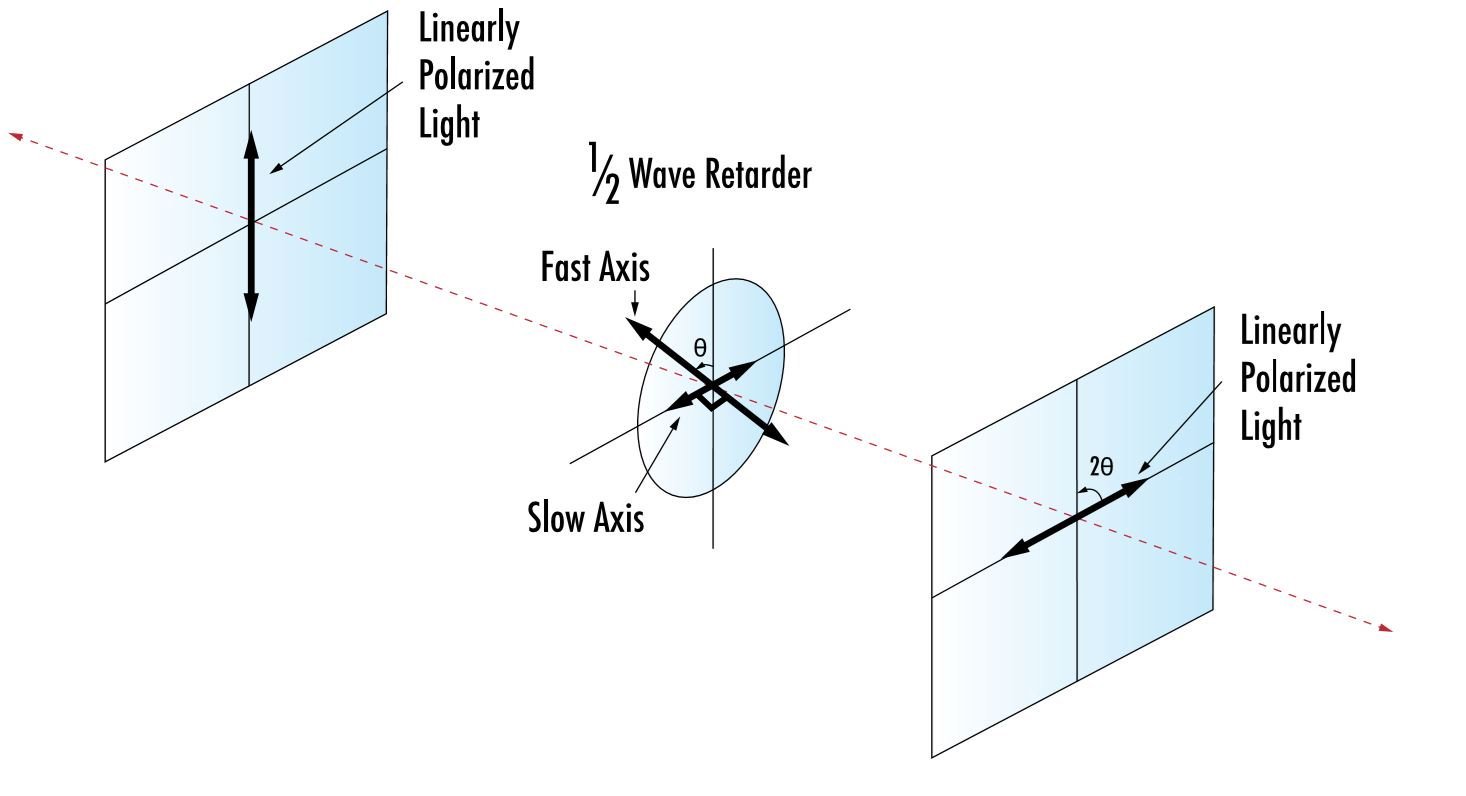
Understanding Retardance in Optics
What is Retardance?
Retardance refers to the difference in optical phase shifts experienced by different polarization components of a light beam propagating through a birefringent medium. It is measured in radians (rad) or degrees (°), or in terms of wavelengths.
Applications of Retardance in Optics
In optics, retardance is commonly introduced using waveplates or retarders to control the amount of retardance. Compensators like Babinet–Soleil and Berek compensators allow for adjustable retardance. When light reflects at a dielectric interface with non-normal incidence, retardance can be calculated using Fresnel equations.
Complex Effects of Retardance
Thermally induced birefringence in materials like laser crystals can lead to position-dependent retardance and axis directions within a beam profile. It’s important to note that retardance is typically wavelength-dependent, although achromatic waveplates aim to minimize this wavelength dependence.
Conclusion
Retardance plays a crucial role in optics, influencing the phase shifts of light beams in birefringent media and at dielectric interfaces. Understanding and controlling retardance is essential in various optical applications.
Source: Edmund Optics
Feel free to comment your thoughts.




