Contents
Source: TOPTICA Photonics AG
The Science Behind Wavemeters
Understanding Wavemeters
A wavemeter, also known as a wavelength meter, is an interferometer used to measure the precise wavelength of laser beams. There are different types of wavemeters, including scanning wavemeters and static devices with no moving parts.
Scanning Michelson Interferometer
One common type of wavemeter is based on a Michelson interferometer. In this setup, light from the laser source is directed into the interferometer, and the length of one of the interferometer arms is scanned. The output power recorded by a photodetector in relation to the arm length changes provides information about the wavelength.
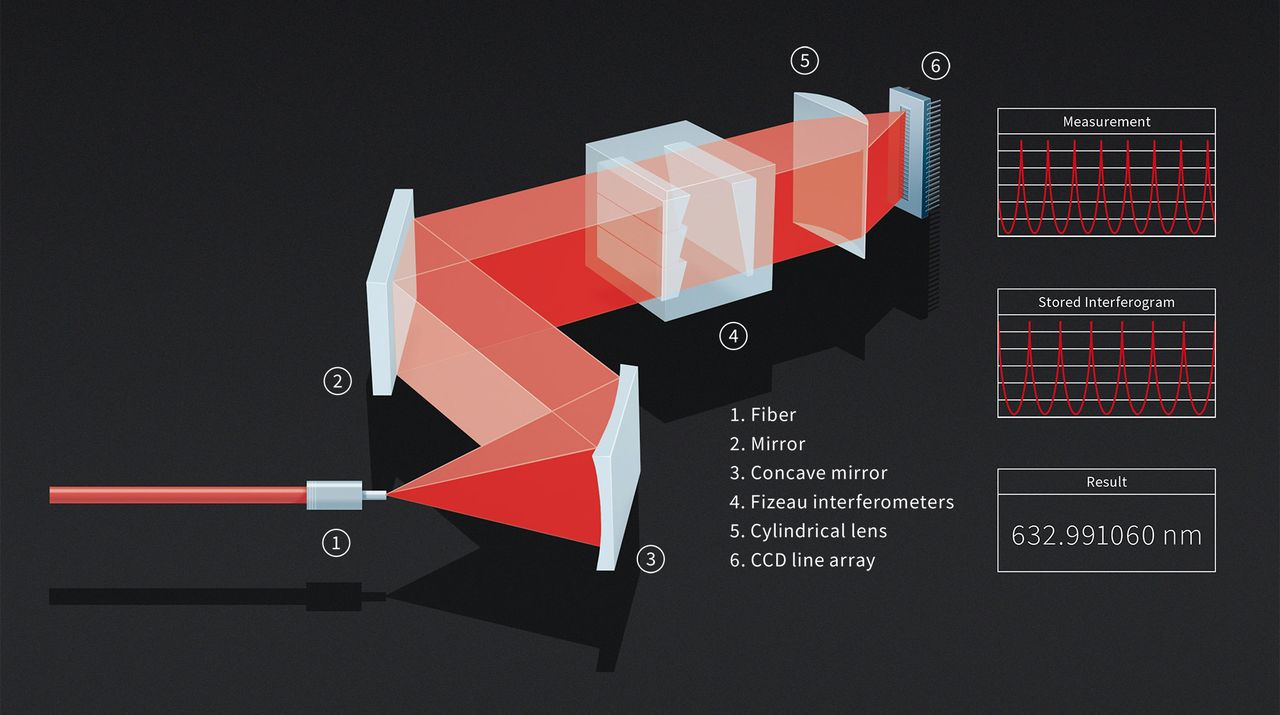
Static Fizeau Interferometer
Another type of wavemeter is the Fizeau interferometer, which utilizes two reflecting surfaces with a slight deviation from parallel. This setup creates an interference pattern that can be analyzed to determine the wavelength of the light.
Measurement Accuracy and Factors Affecting It
Various factors can affect the accuracy of wavelength measurements, including length drifts, imperfections in the scanning mechanism, and fluctuations in optical input power. To improve accuracy, some wavemeters use a stabilized reference laser for comparison.
Vacuum Wavelength vs. Wavelength in Air
There is a difference between wavelengths measured in air and in a vacuum. While interferometric measurements are typically done in air, sophisticated calculations can be applied to determine vacuum wavelengths, which are less dependent on ambient conditions.
Aspects for Selecting a Wavemeter
When choosing a wavemeter, factors to consider include accuracy, measurement speed, input light source, wavelength range, display features, and calibration procedures. Different wavemeters have varying capabilities and are suited for different applications.
Alternative Measurement Techniques
Apart from interferometric wavemeters, other techniques like Fabry–Pérot interferometers and optical frequency measurements can also be used for precise wavelength measurements. Each technique has its advantages and limitations.
Conclusion
Wavemeters play a crucial role in determining the precise wavelength of laser beams, essential for various scientific and industrial applications. Understanding the principles behind wavemeters and the factors influencing their accuracy is key to selecting the right wavemeter for specific measurement needs.

Source: Wikipedia
Feel free to comment your thoughts.



